
Numeric pain scale full#
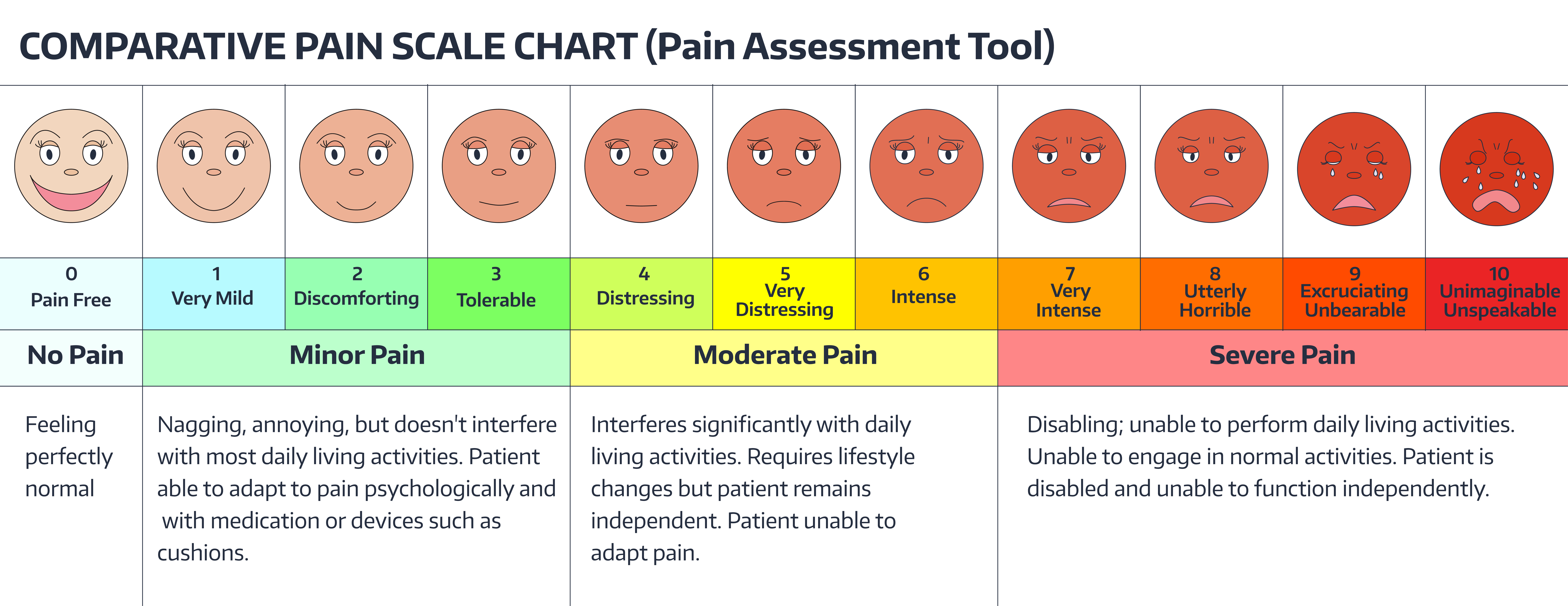
The following were the 5 most frequently diagnosed conditions among the participants Abscess (periapical, periodontal and pericoronal) and space infection (42%), acute apical periodontitis (30%), pulpitis (8%), chronic periodontitis (5%), pericoronitis (3%) (Graph 1).ĭistribution of participants based on the pain scores using full cup test shows majority (60%) of them were in the severe pain category followed by moderate (30%) and mild pain (10%) respectively ( Figure 3).ĭistribution of participants based on the pain scores using numeric pain rating scale shows majority (70%) of them were in the severe pain category followed by moderate (25%) and mild pain (5%) respectively ( Figure 4). More of the study participants (58%) were in the 21–39 age group, females (78%) and had attained a primary level of education (63%). Maximum score (100%) on FCT was given a value of 10 for easy comparison with NPRS. 5 Full Cup Test score was calculated as follows: Height of line/Height of cup × 100 ( Figure 2). And now, how much of this cup is filled by your pain?’ he patients then drew a line on the cup to indicate the level of pain. The patients were told ‘this cup is completely empty when there is no pain and completely full when your pain is the most severe. described the FCT a simple “cup” drawing. Numeric pain rating scale score 0 cm was categorized as no pain, 1–3 cm mild pain (nagging, annoying, interfering little with activities of daily learning ), 4–6 cm moderate pain (interferes significantly with ADLs) and 7–10 cm severe pain (disabling unable to perform ADLs). The NRS, which was developed by Downie in 1978, consists of a vertical or horizontal line, with a total of 11 numbers, ranging from 0 to 10, denoting no pain to the worst possible pain, respectively 4 ( Figure 1). Pain assessment was done for each patient using numeric pain rating scale and full cup test. Data collected included the patient demographic details and the diagnosis of each case was made after proper history taking, clinical examination and radiographic investigation. Young children and adult with communication difficulties, patient with cognitive impairment or delirium were excluded from the study. The study included a total of 60 patients with age range of 12-70 years presented with various forms of orofacial pain to our Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology. FCT is useful for both evaluating and discerning changes in pain and it can be used as a tool in pain assessment. FCT had shown 83 percent sensitivity and 94 percent specificity.Ĭonclusion: Patients who presented with either acute or chronic dental conditions experienced moderate to severe level of pain. The comparison of mean pain scores using full cup test and numeric pain rating scale shows there was significant differences between acute and chronic pain with P- value of 0.023 and 0.005 respectively. Statistical A nalysis and Results: All the data were analysed using inferential statistics Mann Whitney test and the analysis was carried out with SPSS 17. Pain assessment was done for each patient using both numeric pain rating scale and full cup test. Data collected include the patient demographic details and the diagnosis of each case was made after proper history taking, clinical examination and radiographic investigation. Materials and Methods: A total of sixty patients presenting with various forms of orofacial pain were included in this cross-sectional study. Most often pain assessment is considered to be the cornerstone for ideal treatment.Īim and Objective: The aim of this study was to assess the dental patients’ level of pain using Full Cup Test (FCT) and Numeric Pain Rating Scale (NPRS), and to compare and validate the Full Cup Test in the assessment of orofacial pain with Numeric Pain Rating Scale.
The patient’s self-report is the gold standard and it appears to be embedded in everyday clinical practice. Background: Pain intensity is a common outcome domain assessed in pain clinical trials.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
